
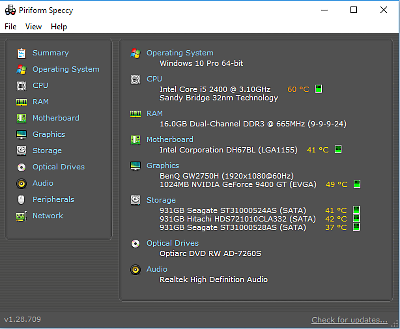
That concluded with “Installation finished. (Do not delete the ~500MB FAT32 partition.) These grub2 partitions will not be reconstructed: you may end up with a ~2MB unallocated space. GParted > Ctrl-R > delete any initial grub2 core.img partitions in /dev/sdc.That confirmed I had a GPT partition table. Go to GParted > menu > View > Device Information.
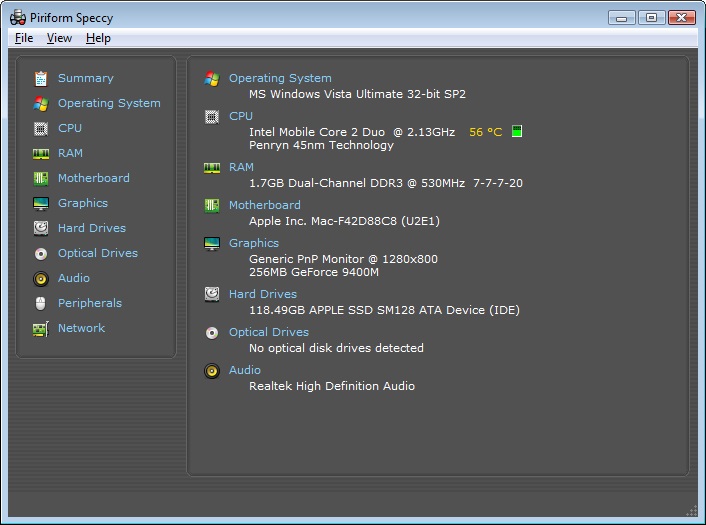
In this case, it was /dev/sdc, because drives installed in the machine I was booting occupied /dev/sda and /dev/sdb at bootup. Run GParted to identify the source drive’s location.In my case, the source drive was an Ubuntu 22.04 LTS installation on a Samsung USB drive. Note that my information may be incorrect or incomplete for others: hence the advice about the clone and/or backup.
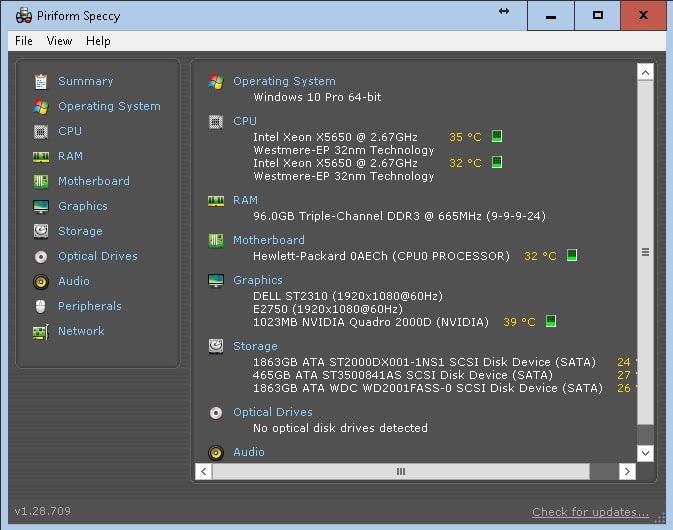
I created my clones and backups using dd. The first step was to work with a clone, or at least have a good backup, of the source drive. (I could use GParted or the Disks utility to see whether the drive was GPT or MBR, a/k/a msdos.) As part of an effort (discussed in another post) to clone a larger Ubuntu USB source drive to a smaller one, it seemed that I might need to convert the source drive from GPT to MBR partition structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
